According to the latest monthly data for the interconnected electricity network from ADMIE (April 2022):
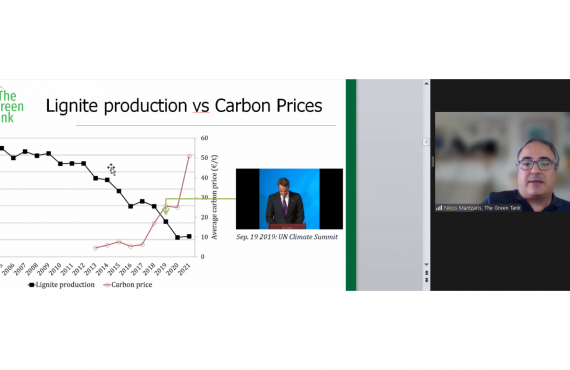
The monthly lignite electricity production (176 GWh) hit an all-time low in April 2022.
At the same time, production from fossil gas (827 GWh) hit a 4-year low, recording the lowest value since April 2018.
On the contrary, renewables (excluding large hydro) (1658 GWh) remained at the very high levels of the previous month, reaching their 3rd highest performance.
Net electricity imports (793 GWh) were also at their highest levels since mid-2020.
Finally, electricity demand in April 2022 (3685 GWh) was the lowest since May 2020, something that combined with the high renewables production, the extremely high fuel prices and the increased net imports, contributed to the low production from lignite and fossil gas.
Thus, in April 2022, renewables (including large hydro) covered 51.2% of the electricity demand, fossil gas 22.4%, net imports 21.5%, while lignite was reduced to just 4.8%.
The predominance of fossil gas in the first three months of the year, was overturned in April. As a result, cumulatively for the first 4 months of the year:
- Fossil gas (5947 GWh) fell to the 2nd place behind renewables (6288 GWh, excluding large hydro) for the second consecutive year.
- Lignite continued its downward trend (1769 GWh), while significantly reduced compared to last year was also the production from large hydro (1454 GWh).
- On the contrary, net imports increased (1966 GWh) compared to the very low levels of 2021.
Overall, in the first four months of 2022, renewables (including large hydro) produced more electricity than fossil fuels (fossil gas + lignite), for the second consecutive year.
For the same period:
The share of renewables without large hydro (36.1%), exceeded that of fossil gas (34.1%).
Net imports covered 11.3% of the demand, while the share of lignite continued its downward trend, covering only 10.2% of the demand, contrary to the 13% of the same period in 2021.
Renewables and fossil gas were the only sources that increased both compared to 2020 and 2021, while energy from renewables exhibited a higher increase compared to 2020 (+29%).
On the contrary, lignite was the only source that decreased compared to both 2020 (-31%) and 2021 (-18%).